OpenAI is following up on last year's announcement of GPTs, the customized versions of ChatGPT, with the launch of two tools. The ChatGPT Team is a new subscription tier that enables collaboration between teams and access to ChatGPT and other OpenAI products, all within a secure workspace where team members can collaboratively create or share their GPTs. The GPT Store is dedicated to simplifying sharing GPTs with other ChatGPT Plus, Team, and Enterprise users.
OpenAI decided to create the ChatGPT Team plan after the success of ChatGPT Enterprise, which is aimed at large organizations requiring secure, scalable deployment and advanced data privacy options. Considering that there may be organizations that may not have the resources or demand for scalable deployment of OpenAI's products but can still benefit from additional privacy and collaboration features not available for ChatGPT Plus subscribers, the ChatGPT Team plan strikes a perfect balance between the Plus and Enterprise subscription tiers.
The ChatGPT plan includes a higher message cap on GPT-4 and services such as DALL·E, Browsing and Advanced Data Analysis; a workplace including an admin console; the possibility of creating and sharing GPTs with the workspace; and the default exclusion of users' data from training. The Team plan lacks Enterprise's unlimited messaging, expanded context window (Team users can access GPT-4 with a 32K context window), SAML SSO, custom data retention windows, advanced admin controls, and priority support. Still, ChatGPT Team is a feature-rich plan thought to be a solid alternative for smaller teams to collaborate and securely benefit from OpenAI's products without trying to navigate the risks associated with using individual ChatGPT Plus subscriptions.
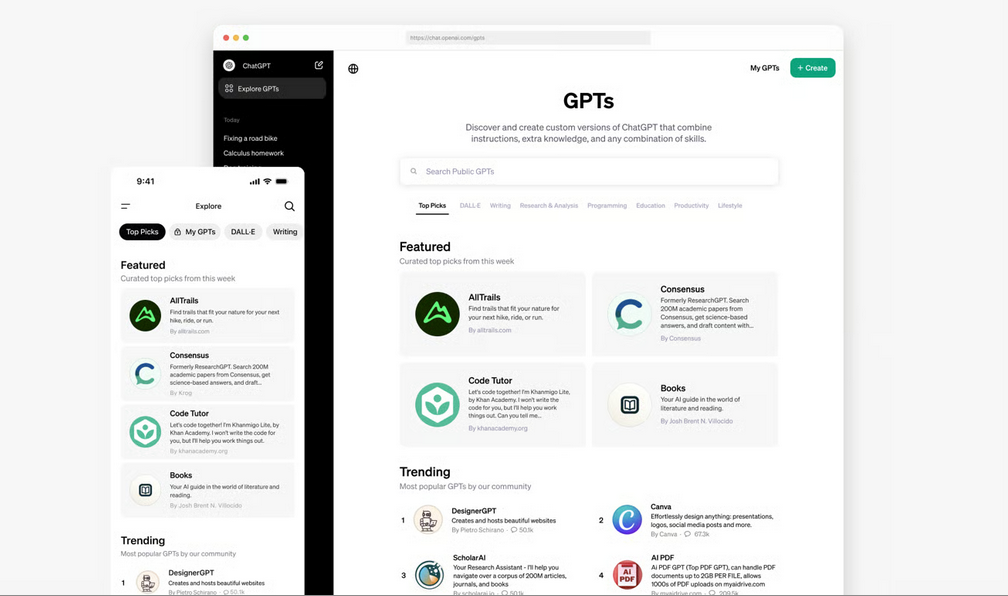
Another attractive feature is the capability to create and share GPTs in the collaborative workplace, thus eliminating the need for individual users to customize ChatGPT to assist with the same workflow or even having to individually look for specific GPTs in the newly created GPT Store, which is clearly meant to have a wider reach than sharing custom versions of ChatGPT within a single organization. In addition to helping users navigate the more than 3 million custom ChatGPT versions created since the GPTs functionality was first introduced in November last year, the GPT Store also includes a private section for Team and Enterprise users from which administrators can manage GPTs securely published to the workplace. Enterprise admins can even control how internal GPTs are shared and which external GPTs can be used within the organization.
Other interesting GPT Store functions include the community leaderboard featuring popular and trending GPTs, category-based browsing, weekly GPT highlights showcasing impactful GPTs, and the Builder revenue program to be launched in Q1. Some of the first featured GPTs include personalized trail recommendations with AllTrails, the Khan Academy Code Tutor, and Canva's design assistant. Getting a GPT into the Store requires two simple steps: users must have a verified Builder Profile and save their GPTs for "Everyone" rather than "Anyone with a link". Submitted GPTs will be reviewed for policy compliance, and users can always report harmful GPTs.
It is interesting to note that by announcing these new services, OpenAI is simply extending its subscription plans to attract a demographic that was previously excluded (small teams requiring a solution more sophisticated than ChatGPT Plus but less than Enterprise) and creating a platform that guarantees that a substantial number of LLM applications will be covered by a GPT, thus reducing the need to look outside the OpenAI ecosystem for solutions such as coding tutors, design assistants, or even writing coaches. It is difficult not to think these moves were performed to keep OpenAI's reign as the dominant generative AI provider intact.






Comments