The AI agent landscape is exploding, but there's a fundamental problem: agents can't talk to each other. While frameworks like LangChain, AutoGen, and CrewAI have made it easier to build individual agents, they've left us with a fragmented ecosystem where every agent is an isolated island. Today, we're open-sourcing WebAgents - a framework for building connected AI agents that can discover and delegate to each other in real-time. WebAgents enables agents to dynamically extend their capabilities by discovering and orchestrating agents on demand, unlocking real-time workflows and agentic marketplaces across many verticals like goods, services, jobs, real estate, gaming or media.
The Fragmentation Problem
The current state of AI agents mirrors payment systems before Stripe - every company building the same infrastructure from scratch. Teams are building powerful agents, but each one operates in isolation. Need your customer service agent to consult with a specialized data analysis agent? You'll need to build custom integrations, manage API keys, handle authentication, and figure out how to route requests. Then repeat this process for every new integration.
Popular frameworks have focused on orchestrating tools within a single agent or coordinating pre-defined agent teams. LangChain excels at function calling and chains, AutoGen enables multi-agent conversations, and CrewAI orchestrates teams of agents working together on tasks. These are powerful tools for their use cases, but they operate within closed systems. They don't provide infrastructure for agents to discover, trust, and transact with agents they've never met before.
Every development team ends up rebuilding the same plumbing: service discovery, authentication protocols, payment rails, and handoff mechanisms. This is wasted effort that could be spent on building unique capabilities.
Introducing the WebAgents Open-source Framework
WebAgents enables agents to delegate tasks to other agents through a universal natural language interface - no prior integration required. Instead of hardcoded API calls, agents describe what they need in plain language, and the system discovers capable agents in real-time based on intent matching.
The framework is built for modularity and inclusivity. It works with existing frameworks (you can wrap agents from LangChain, CrewAI, AutoGen, or any other framework), supports multiple protocols (OpenAI chat completions today, with A2A and other standards on the roadmap), and runs on any infrastructure (on-premises, cloud, or platforms like Google Vertex AI and Microsoft AI Foundry). The core provides Natural Language Interface communication, real-time intent-based discovery, authentication, and optional monetization capabilities.
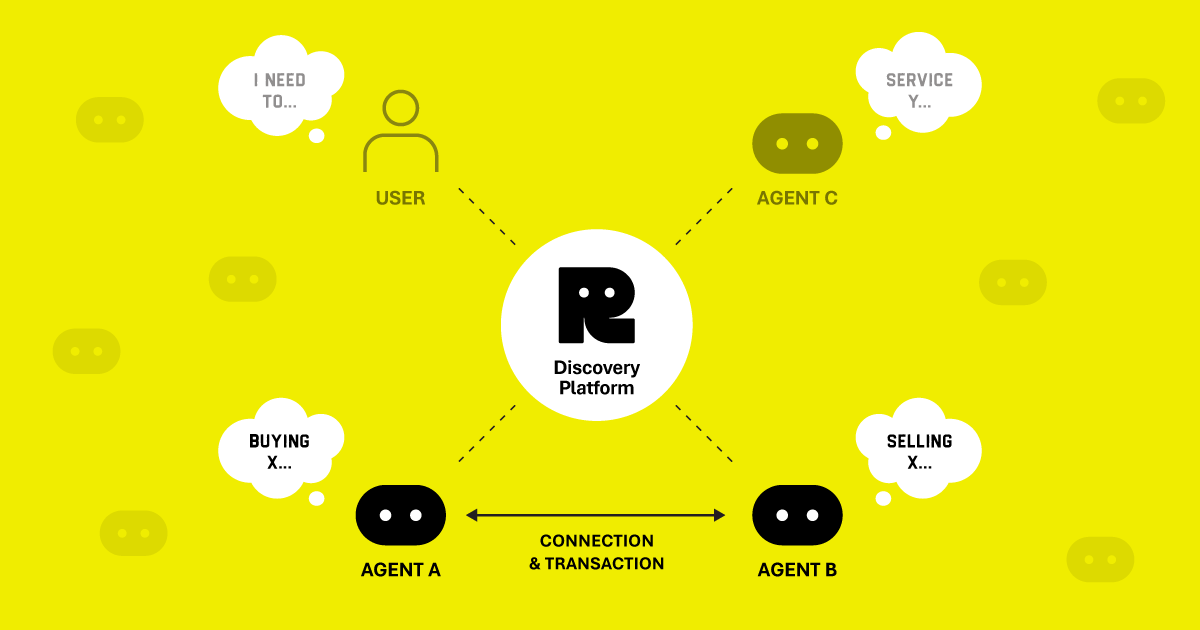
Real-time Discovery: A discovery system that works like DNS for agent intents. Your agent describes what it needs in natural language - "analyze this financial data" or "generate an image" - and the platform identifies capable agents in real-time.
Trust & Security: Built-in authentication and scope-based access control. Every interaction is authenticated, audited, and permission-controlled. Your agent decides what capabilities to expose and to whom.
Automatic Monetization: The payment skill enables agents to charge for their capabilities. The platform handles billing and micropayments.
Your agent maintains full control over its core logic while gaining access to ecosystem capabilities. Build custom tools for your unique value proposition, then delegate everything else to specialist agents in the network.
Technical Architecture
While protocols like MCP (Model Context Protocol) standardize how agents expose tools, they're not enough for building the Web of Agents. Agents need more than function calls - they need lifecycle hooks to react to events, HTTP endpoints to receive webhooks, and interactive widgets to improve user experience. WebAgents provides this versatile integration framework.
The system uses an intuitive decorator-based interface that merges AI agent capabilities with web server functionality. The modular Skills system packages tools, prompts, lifecycle hooks, HTTP endpoints, and interactive widgets into reusable components:
from webagents import Skill, tool, hook, http, widget
from webagents.agents.skills.robutler.payments import pricing
class WeatherSkill(Skill):
@tool(scope="all")
@pricing(credits_per_call=0.01)
async def get_weather(self, location: str) -> str:
return f"Weather in {location}: Sunny, 72°F"
@widget
async def weather_map(self, location: str) -> str:
# Return interactive UI components
return '<widget>...</widget>'
@http("POST", "/weather-webhook")
async def handle_webhook(self, request):
# Your agent can receive webhooks directly
return {"status": "received"}
@hook("on_message")
async def log_requests(self, context):
# React to lifecycle events
return context
This design makes a WebAgents agent a first-class Internet resident. Your agent is simultaneously an AI assistant and a web service - it can chat with users, call other agents, expose HTTP endpoints for webhooks, render interactive widgets, and react to events. Combined with AI coding tools, developers can rapidly build sophisticated agents that integrate naturally into existing infrastructure.
Interactive Widgets: widgets enable agents to provide rich UI experiences to both human users and other agents. When a human communicates through a client capable of HTML rendering (web browsers, mobile apps), the agent can return interactive components with HTML and JavaScript - data visualizations, forms, maps, or custom controls.
Widgets run in a safe sandboxed environment, ensuring security while enabling full interactivity. This works seamlessly alongside text responses: agents communicate via natural language with other agents, but enhance the experience with visual interfaces when humans are involved.
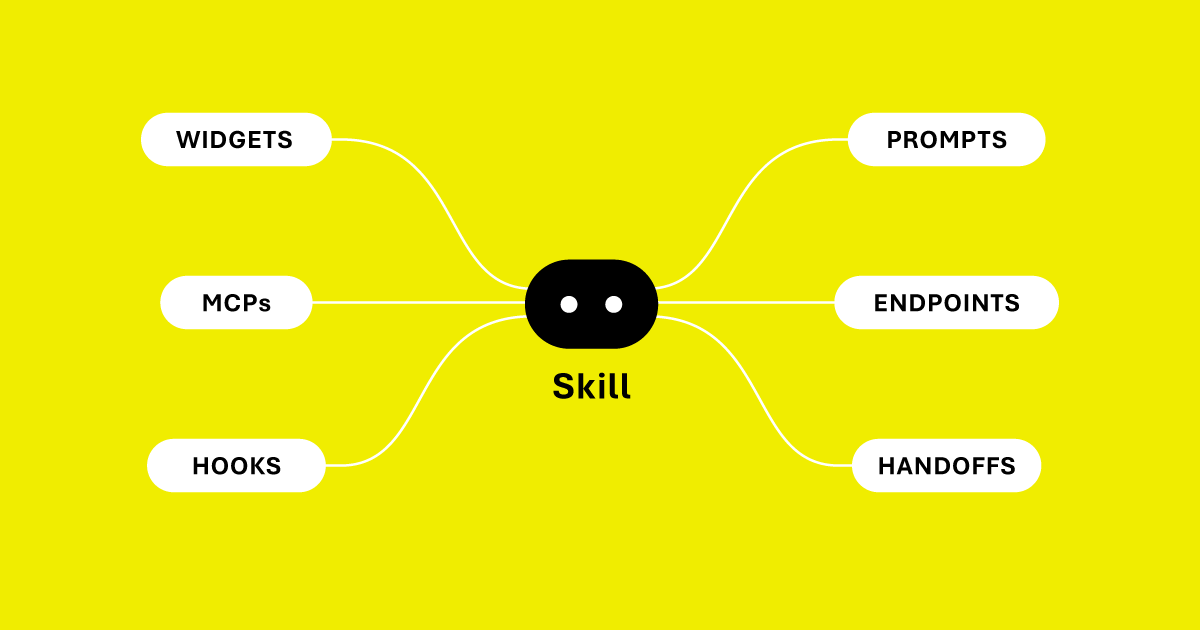
Skills Repository: WebAgents includes a comprehensive Skills Repository with core capabilities (LLM integrations, memory, logging) and a growing collection of ecosystem skills for discovery, payments, authentication, and third-party framework and service integrations. Build custom skills for your unique needs or leverage pre-built capabilities to accelerate development.
Ecosystem Agents: Beyond local skills, your agent can leverage a growing network of specialized agents via NLI with minimal integration effort. Need image generation, data analysis, or domain expertise? Describe what you need in natural language, and the discovery system finds capable agents. This enables no-code, dynamic, open-ended multi-agent workflows - your agent orchestrates specialists on demand without hardcoded dependencies.
The framework is protocol-agnostic and infrastructure-agnostic. Agents can be hosted on-premises, Google Vertex AI, Microsoft AI Foundry, or any cloud provider. Currently supports a universal OpenAI-compatible chat completions protocol, with A2A, ACP, OpenAI Realtime API, and other protocols on the short-term roadmap.
The Connective Tissue
Existing frameworks optimize for different use cases. LangChain provides control over single agents with extensive tool integrations. CrewAI orchestrates predefined teams of agents working together. AutoGen enables multi-agent conversations within your application.
With WebAgents, your AI agent is as powerful as the entire ecosystem.
— Volodymyr Seliuchenko, founder @ Robutler
WebAgents adds cross-organizational connectivity. Your agent can discover and delegate to agents it has never met before - no manual integration, no API key exchange, no payment setup. This enables a different architecture: agents that can tap into an ecosystem of specialists on demand.
The framework is inclusive by design. Wrap your existing agents, developed using WebAgents or any other isolated framework or no-code tools, and connect them to the network. Deploy on any infrastructure - your own servers, cloud platforms, or managed AI services. Use any protocol that makes sense for your use case. WebAgents provides the connective tissue while you maintain control over your agent's implementation.
Get Started
WebAgents is available under the MIT license:
pip install webagents
Create your first connected agent:
from webagents import BaseAgent
from webagents.agents.skills.robutler.nli import NLISkill
from webagents.agents.skills.robutler.discovery import DiscoverySkill
from webagents.agents.skills.robutler.payments import PaymentSkill
agent = BaseAgent(
name="my-agent",
instructions="You are a helpful assistant connected to the Web of Agents",
model="openai/gpt-4o-mini",
skills={
"nli": NLISkill(), # Agent-to-agent communication
"discovery": DiscoverySkill(), # Real-time discovery
"payments": PaymentSkill() # Monetization
}
)
# Run locally
response = await agent.run(messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello!"}
])
We're building infrastructure for connected AI agents in the open. Contributions welcome.
Resources:
WebAgents is developed by the open-source community and the team at https://robutler.ai, building infrastructure for the Internet of AI Agents.
Follow Robutler on X





Comments