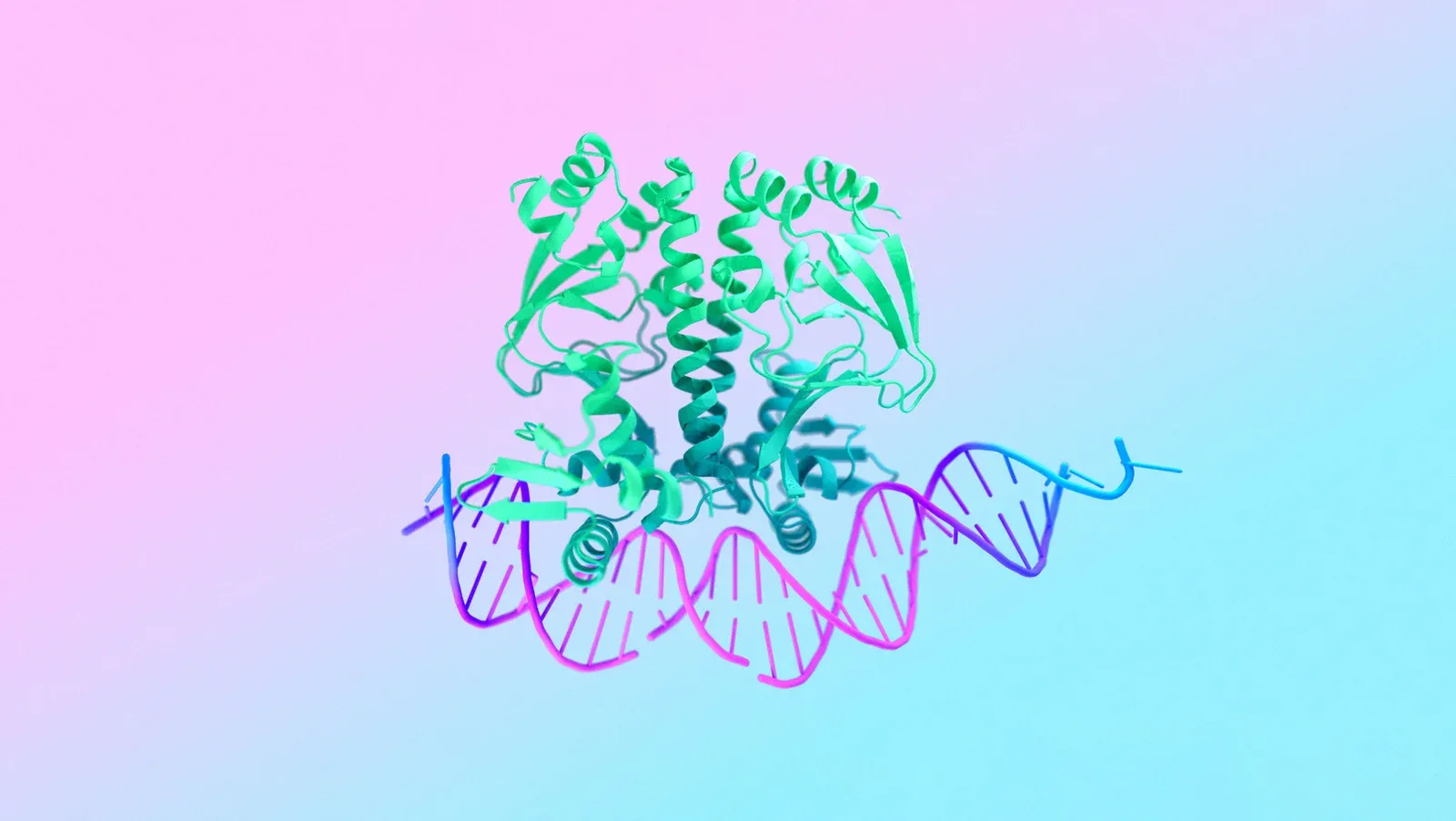
Google DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs recently introduced AlphaFold 3 in a paper published in Nature which showcases the model's capabilities to predict the structure and interactions of biomolecules accurately, including large biomolecules like proteins, DNA, and RNA and smaller ones, like ligands, a category of molecules to which many drugs belong. These capabilities make AlphaFold 3 well-suited for assisting in drug discovery and design. Isomorphic Labs is already tapping into this potential, looking into promising internal projects and collaborating with other pharmaceutical companies. AlphaFold 3 builds on the achievements of AlphaFold 2, which has contributed to research projects including malaria vaccines, cancer treatments, and enzyme design. AlphaFold has been cited over 20,000 and its contributions have been recognized with multiple prizes, including the Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences.
Unlike its predecessors, AlphaFold 3 was trained on a dataset including all biomolecules. Moreover, its architecture includes an improved Evoformer module, the architecture responsible for AlphaFold 2's groundbreaking performance. Thanks to its upgraded architecture, AlphaFold 3 can process input lists of molecules and assemble predictions using a diffusion model similar to the ones used in image generation engines. The generation process builds a predicted structure beginning with a cloud of atoms, overlaying a structure refined over multiple steps.
This process results in a broad and accurate approach that surpasses all existing methods. In particular, AlphaFold 3 predicts drug-like interactions, a class of processes that includes protein-ligand and protein-target antibody bindings, with remarkable accuracy. The model is 50% more accurate than the best physics methods on the PoseBusters benchmark and it does not require any structural information as input. Thus, AlphaFold 3 is the first AI approach to molecule structure prediction to surpass physics-based approaches. To make AlphaFold 3's groundbreaking performance to a wider audience of researchers, Google DeepMind announced the launch of AlphaFold Server, a free platform for non-commercial research.
AlphaFold Server joins DeepMind's free database of 200 million protein structures to reflect Google's commitment to sharing AlphaFold's potential with the world. The company is also expanding its AlphaFold online tutorial in collaboration with EMBL's European Bioinformatics Institute and organizations in the Global South to accelerate the model's adoption and research on underfunded areas including rare or neglected diseases and food security. The expansion of the educational resources, and Google DeepMind's mission to safely deploy AlphaFold, will empower scientists to tap into AlphaFold's potential to accelerate research programs and open up new lines of research.



Comments