Welcome to this week's edition of Data Phoenix Digest! This newsletter keeps you up-to-date on the news in our community and summarizes the top research papers, articles, and news, to keep you track of trends in the Data & AI world!
Be active in our community and join our Slack to discuss the latest news of our community, top research papers, articles, events, jobs, and more...
Data Phoenix's upcoming webinars:
Gorilla: Large Language Model Connected with Massive APIs
The Gorilla project is designed to connect large language models (LLMs) with a wide range of services and applications exposed through APIs. Imagine if ChatGPT could interact with thousands of services, ranging from Instagram and Doordash to tools like Google Calendar and Stripe, to help you accomplish tasks. This may be how we interact with computers and even the web in the future. Gorilla is an LLM that we train using a concept we call retriever-aware training (RAT), which picks the right API to perform a task that a user can specify in natural language. Gorilla also introduces an Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) based sub-tree matching algorithm, which for the first time allows us to measure hallucination of LLMs!
Speaker: Shishir is a Ph.D. student in Computer Science at UC Berkeley advised by Joseph Gonzalez and Prabal Dutta affiliated with the Sky Computing Lab (previously RISE), Lab11, and Berkeley AI Research (BAIR). He is broadly interested in ML-Systems, and LLMs. Previously he has interned at Google Brain, and Amazon Science, and was at Microsoft Research as a Research Fellow before.
- Trends and Applications of AI/ML and Analytics in Sports
Rajesh Kumar (Assistant Professor, Woxsen University) / October 5 - Large Language Models for Program Synthesis
Xinyun Chen (Research Scientist at Google DeepMind) / October 16 - Lessons Learned from Building a Managed RAG Solution
Denys Linkov (ML Lead at Voiceflow) / October 19 - Using memory with LLM applications in production
Sergio Prada (Co-founder and CTO at Metal) / October 26 - MLOps for Ads Ranking at Pinterest
Aayush Mudgal (Senior ML Engineer at Pinterest) / October 31
Stand with Data Phoenix in the AI Revolution
From fresh startups to global enterprises - the world is abuzz with AI. Yet, critical information can easily be missed in the noise. By subscribing to Data Phoenix Premium, you can support our mission to provide comprehensive AI coverage.
Ignite your knowledge with Data Phoenix.
Summary of the top articles and papers
Articles
LLM Monitoring and Observability — A Summary of Techniques and Approaches for Responsible AI
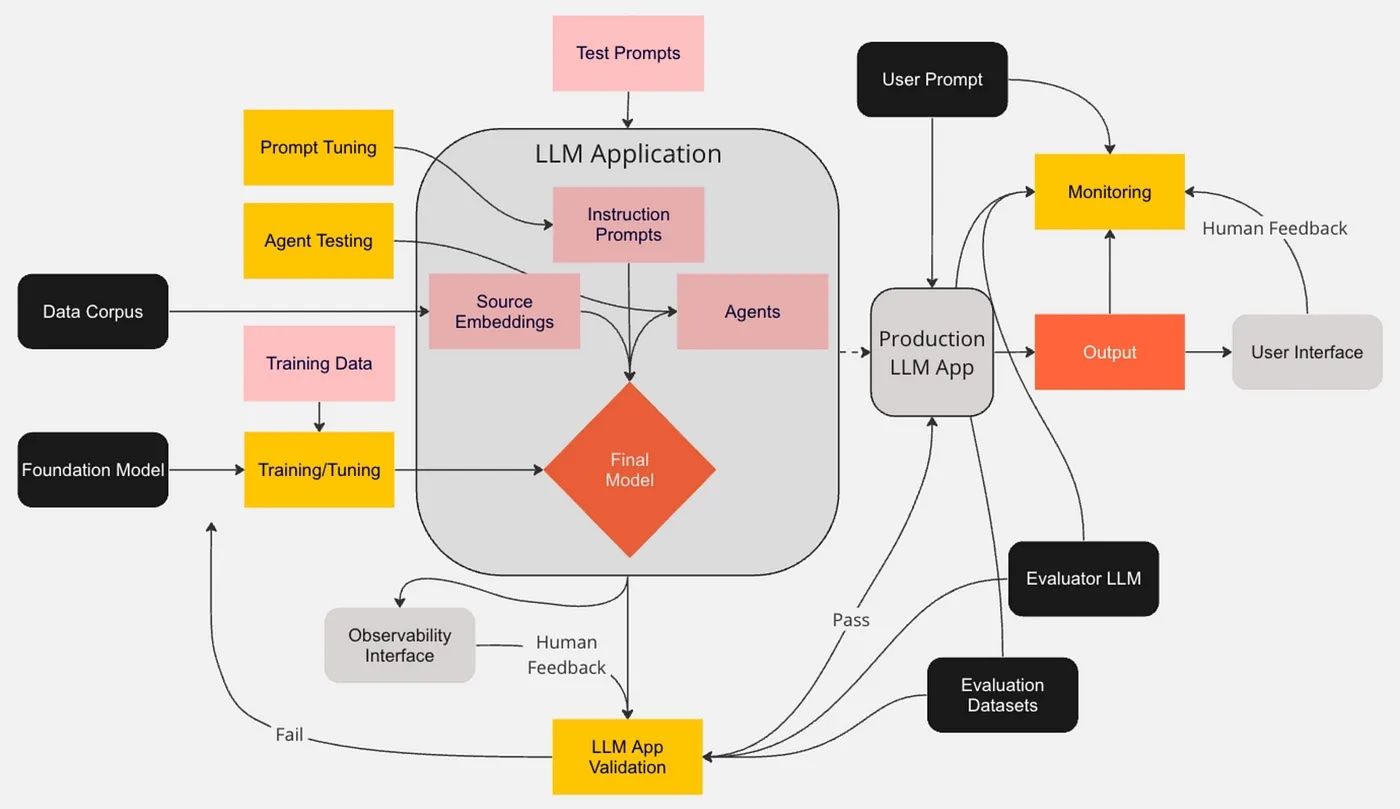
The author spent hours reading documentation, watching videos, and reading blogs from software vendors and open-source libraries specializing in LLM monitoring and observability. In this article, he summarizes his research on large language model (LLM) monitoring.
Fine-tuning Llama 2
The launch of Llama 2 has generated a lot of buzz. Paired with LangChain and vector databases, Llama 2 offers immense possibilities for a range of applications. In this article, you’ll learn how to fine-tune llama-2-7b-chat-hf using dstack.
Building LLM applications for production
This article explores the challenges and potential of LLMs in ML workflows. It's divided into three parts: 1 examines the difficulties of productionizing LLMs; 2 details methods for composing applications with control flows and tools; 3 highlights LLM use cases.
Building Your Own DevSecOps Knowledge Base with OpenAI, LangChain, and LlamaIndex
The article delves into DevSecOps and explores building a custom knowledge base for DevSecOps. By utilizing tools like OpenAI, LangChain, and LlamaIndex (GPT Index), the author guides readers through the process, step by step.
Replicate ChatGPT Training Quickly and Affordable with Open Source Colossal-AI
Colossal-AI enables you to use it as a framework for replicating the training process of OpenAI’s popular ChatGPT application optimized for speed and efficiency. This article goes deep into how all of its components work together. Check out this exciting read!
ML Model Packaging [The Ultimate Guide]
ML model packaging is an essential component of the ML lifecycle. Ensuring its proper implementation can impact the success of a deployment. This guide delves into the concepts, challenges, and best practices surrounding ML model packaging. Check it out!
Papers & projects
Agents: An Open-source Framework for Autonomous Language Agents
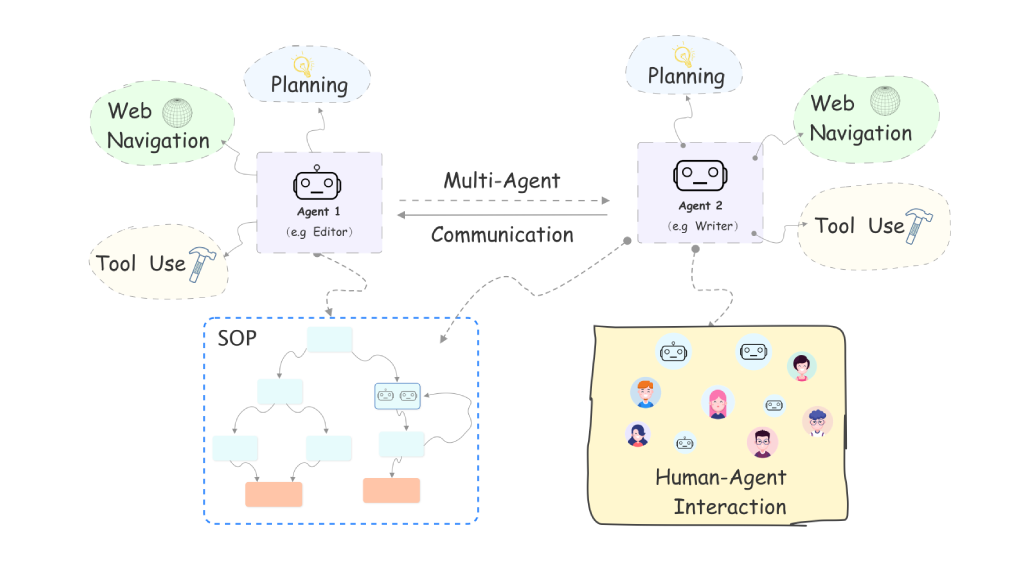
Agents is an open-source library designed to make it easy for a non-specialist audience to build autonomous language agents that can automatically solve various tasks and interact with environments, humans, and other agents using natural language interfaces.
LEDITS: Real Image Editing with DDPM Inversion and Semantic Guidance
LEDITS is a combined lightweight approach for real-image editing, incorporating the Edit Friendly DDPM inversion technique with Semantic Guidance, to extend Semantic Guidance to real image editing, while harnessing the editing capabilities of DDPM inversion.
RT-2: Vision-Language-Action Models
Vision-language models trained on Internet-scale data can be incorporated into end-to-end robotic control to boost generalization and enable semantic reasoning. The authors propose to co-fine-tune models on robotic trajectory data and Internet-scale vision-language tasks.
DragDiffusion: Harnessing Diffusion Models for Interactive Point-based Image Editing
In this work, the authors extend DragGAN to diffusion models and propose DragDiffusion, improving the applicability of interactive point-based editing in real world scenarios and optimizing the diffusion latent to achieve precise spatial control. Take a look how they did it!
ConsistentNeRF: Enhancing Neural Radiance Fields with 3D Consistency for Sparse View Synthesis
ConsistentNeRF is a method that uses depth information to regularize pixel multi-view and single-view 3D consistency. It uses depth-derived geometry info and a depth-invariant loss to concentrate on pixels that exhibit 3D correspondence and maintain consistent depth relationships. The approach can enhance model performance in sparse view conditions
MagicEdit: High-Fidelity Temporally Coherent Video Editing
MagicEdit is a new approach, allowing to disentangle the learning of appearance and motion to achieve high-fidelity and temporally coherent video editing. It supports various editing applications, including video stylization, local editing, video-MagicMix, and video outpainting.






Comments