This Week in AI: March 24–30
Upcoming Grok-1.5 early preview; MIT starts working group on Gen AI and the Work of the Future; Microsoft announces security and trustworthiness-boosting tools in Azure; Amazon concluded its $4B investment in Anthropic; NVIDIA crushed MLPerf's newest inferencing tests; and more.
Every weekend, we bring together a selection of the week's most relevant headlines on AI. Each weekly selection covers startups, market trends, regulation, debates, technology, and other trending topics in the industry.
The Grok-1.5 early preview is coming soon
The release of Grok-1's model weights and network architecture gave the world a glimpse of xAI's progress at building a 'spicy' question-answering alternative to ChatGPT. Shortly after that release, the company announced the upcoming availability (on the X platform) of Grok-1.5, the next iteration of its chatbot. Grok-1.5 features longer context understanding and advanced reasoning capabilities. Grok-1.5 significantly improved performance in coding and mathematical reasoning tasks compared to its predecessor. Grok-1.5 performs slightly better overall than the new Claude 3 Sonnet but still lags behind the more powerful Claude 3 Opus, Gemini 1.5, and GPT-4. The new 128K-token context window is also a welcome addition and a necessary one if Grok is meant to take on the dominant foundation models. The expanded context window allows Grok to handle longer and more complex prompts without compromising its retrieval and instruction-following capabilities. Grok-1.5 will be available as an early preview, but xAI expects to release new features as the chatbot is rolled out to wider audiences.
The MIT announced that it will convene a working group on Generative AI and the Work of the Future
The working group's activities will aim to answer questions regarding the impact that generative AI will continue to have on the way we work. Specifically, the working group will be tasked with finding ways that generative AI can lead to better jobs. Currently, the group features 25 organizations and non-profits collaborating with MIT faculty and students to compile original data on the use and impact of generative AI tools in the workplace. The workgroup is organized at MIT’s Industrial Performance Center (IPC) under the leadership of IPC Executive Director Ben Armstrong and MIT professors Julie Shah and Kate Kellogg. Since its inception, the working group has already launched Generation AI, a monthly newsletter devoted to sharing the group's early findings, held a first meeting of AI leads from a selection of global organizations, and hosted a workshop on responsible AI practices jointly with MIT’s Industrial Liaison Program.
Google.org funds the working group as part of its Digital Futures Project. Over the next couple of years, the working group will focus on three activities: conducting research on early use cases of generative AI at organizations around the globe, hosting quarterly meetings and some in-person summits to foster the exchange of ideas and experiences among its members, and develop training materials for organizations preparing to upskill or retrain their workers as they incorporate generative AI into their workflows. MIT graduate student Work of the Future Fellows are already collaborating with member organizations to perform the research required for the first activity, with a special focus on the steps that organizations are taking to ensure the responsible use of generative AI tools and how the introduction of these tools is transforming the sets of skills and training that workers need to do well at their jobs. The results of this research will be published as a series of case studies throughout the year.
SydeLabs announces a $2.5M seed funding round
SydeLabs' funding round was led by RTP Global, with participation from Picus Capital and a selection of angel investors. The company has declared that the raised funds will go into R&D and building the company's product portfolio. SydeLabs was founded by Ruchir Patwa and Ankita Kumari in 2023 and, since then, the company has focused on helping its customers identify vulnerabilities in their LLMs and applications before they go into production. The startup's portfolio comprises three AI-focused security products: SydeBox, currently in beta, and the upcoming SydeGuard and SydeComply. SydeBox is a self-service read teaming solution that lets users perform a series of assessments of their apps and models to verify that they are not susceptible to vulnerabilities. On the other hand, SydeGuard and SydeComply are meant to be real-time scanners that provide intent-based protection in the case of the former and notify or attempt to fix gaps that could lead to compliance issues for the latter.
Metaview secured $7M in Series A funding
The company specializes in developing tools that assist recruiters throughout the hiring process, from the first interview to the candidate debrief. Metaview's main offerings are tools for automated notetaking and a conversational assistant touted as "ChatGPT for interviews" that provides answers about candidates and recruiting processes. Metaview's Series A was led by Plural, with participation from Zach Coelius, Vertex Ventures US, Seedcamp, Village Global, and some angel investors. The company is reportedly leveraging the funding to grow its team by opening positions across the Product and Engineering, Sales, and Marketing areas.
Microsoft announces security and trustworthiness-boosting tools for generative AI applications building in Azure
The announced tools are available or coming soon to the Azure AI Studio:
- Prompt Shields, including a new model that identifies indirect prompt attacks before they affect the user's models, is available for preview in Azure AI Content Safety.
- Groundedness detection to detect hallucinations in outputs is upcoming.
- Safety system messages to redirect a model toward safer behaviors, coming soon.
- Safety evaluations to determine the vulnerability of an application to jailbreak attacks and generating content risks, in preview.
- Risk and safety monitoring is in preview for the Azure OpenAI service, coming soon for other models.
Together, these tools are meant to assist users in safely developing and deploying generative AI applications across their complete lifecycle.
Robovision secured $42M to accelerate its AI-powered computer vision platform
The round was led by Target Global and Astanor Ventures, with Red River West as a participant. With this investment round, Robovision's raised funding adds up to $65 million. The Ghent-based startup offers end-to-end no-code computer vision solutions for manufacturers and production lines. Robovision's partnership with ISO Group helps plant 1 billion tulips yearly, about 50% of the world's production. Robobovision also assists Hitachi in the manufacturing of semiconductor wafers. One of the company's biggest selling points is that it can upgrade existing infrastructure with computer vision. This translates into minimal hardware adjustments and the possibility for customers to create and maintain personalized models. The funding round will help Robovision strengthen its US presence and accelerate local market growth and R&D efforts.
Amazon concluded the previously announced $4B investment in Anthropic
Last September, Amazon and Anthropic announced a strategic collaboration to advance the development of generative AI. In a nutshell, Anthropic committed to training its models using Amazon's Trainium and Inferentia chips, using AWS as its primary cloud service provider, and making its models available to AWS customers via Amazon Bedrock. In exchange, Amazon would invest up to $4B in Anthropic and would have its developers and engineers build new customer experiences using Anthropic's models on Amazon Bedrock. Among the many fruits of the collaboration, a very varied and ever-increasing roster of organizations are building their AI applications using Claude via Amazon Bedrock, including ADP, Broadridge, Clariant, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Delta Air Lines, Perplexity AI, Pfizer, the PGA TOUR, Ricoh USA, and Siemens. More recently, AWS, Accenture, and Anthropic announced they would be helping enterprises and organizations scale their AI applications safely and responsibly. Now, Amazon is announcing that it has followed on its September 2023 $1.25B investment with an additional $2.75B, thus completing the originally agreed-upon $4B investment.
ValidMind raised $8.1M in seed funding to automate model documentation and enhance AI risk management and governance processes
The oversubscribed seed funding round was led by Point72 Ventures, with backing from Third Prime, AI Fund, FJ Labs, New York Life Ventures, Notion Capital, Angel Invest Ventures, and Gaingels. Point72 Partner Tripp Shriner will join ValidMind's board of directors. The funds will enable the startup to continue the development of its AI and Model Risk Management solution, currently geared toward banks and financial institutions. Ultimately, ValidMind aims to become the certifying authority of all AI solutions.
NVIDIA crushed MLPerf's newest inferencing tests: Llama 2 70B and Stable Diffusion XL
On the latest version of the benchmark tests, NVIDIA dominates the scorecards, followed by Qualcomm and Intel accelerators. MLPerf benchmarks represent a variety of model sizes. Last year, the 6 billion parameter text summarization benchmark GPT-J was added to the roster and represented the first push into the LLM realm. The text-to-image Stable Diffusion XL model, at 2.6 billion parameters, and Llama 2, at 70, will now join the MLPerf battery of tests. These benchmarking tests are divided between systems used in data centers and systems meant for consumer applications. Each test can be carried out online in idealized circumstances to find the likely maximum performance, or on a more realistic online setting that simulates, for instance, queries in a data center setup. The NVIDIA H200 and H100 were the top performers in the data center inference category, likely because Version 4.0 of the MLPerf benchmark did not sample the upcoming NVIDIA Blackwell architecture. NVIDIA was also a top-edge (real-world) inference category contender. Finally, Qualcomm and NVIDIA went head to head on the energy efficiency benchmarks (again, pending testing against NVIDIA Blackwell).
Observe closed a successful Series B round
Observe Inc. recently announced that it raised $115 million in a Series B round led by Sutter Hill Ventures, backed by existing investors Capital One Ventures and Madrona, and joined for the first time by Snowflake Ventures. Observe has been lauded for its Observability SaaS platform. The Series B was raised at a valuation 10x higher than the one for the company's Series A round. The company has been growing by all metrics, and the Series B round will likely contribute to accelerating that growth. Observe has successfully positioned itself as a solid alternative to traditional observability tools. Unlike the latter, which requires multiple data stores, can only troubleshoot known issues, needs human-fed context, lacks satisfactory retention rates, and is locked to ingest-based pricing, Observe breaks away from that mold to provide a solution that only requires a single data store, can troubleshoot known and unknown problems, features built-in context and attractive retention rates, and allows to choose between ingest-based and usage-based pricing.
A research team in Belgium is leveraging AI to figure out what makes a beer taste good
Led by KU Leuven's Prof Kevin Verstrepen, the research team's goal was to examine the close relationship between aroma and perception. The way food tastes to us is partly the result of the perception of certain aromatic compounds present in them. However, it is not only the concentration of any given compound that affects the result, some aromatic compounds also interact among themselves, with the presence of a given compound being able to, for example, transform the way another one is perceived. Naturally, beer is only a particular instance of these general phenomena and an interesting one to investigate, given the cultural significance of Belgian beers. The research team first prepared a dataset containing the chemical makeup of over 250 commercial Belgian beers belonging to 22 different varieties.
The set contained data on features such as alcohol content, pH, sugar concentration, and the presence and concentration of over 200 aromatic compounds known to affect the taste of a beer. A second data set was started with the scores and ratings of a 16-member tasting panel that rated the 250 beers for 50 attributes. This process alone took three years. The researchers collected 180,000 reviews from the RateBeer platform to complement the tasting data ratings. The research team found that while overall preference was biased by price, ratings about the beers' specific attributes correlated with those of the tasting panel. Once the datasets were ready, the team built machine-learning models that could predict how a beer would taste and its level of appreciation, based on its composition. To test the model's output, the researchers spiked beers with the substances flagged by the model as predictors of appreciation. When the tasting panel was asked to rate the spiked beers, their ratings were consistently higher than the ones granted to the non-spiked beer.
Prof Verstrepen stated that although the models had limitations, a potential application was to tweak non-alcoholic beers to improve their quality. Additionally, he recognized that while machine learning models could assist in optimizing the quality of beers, it was still up to the brewer's mastery to develop a recipe and carry out the process successfully.
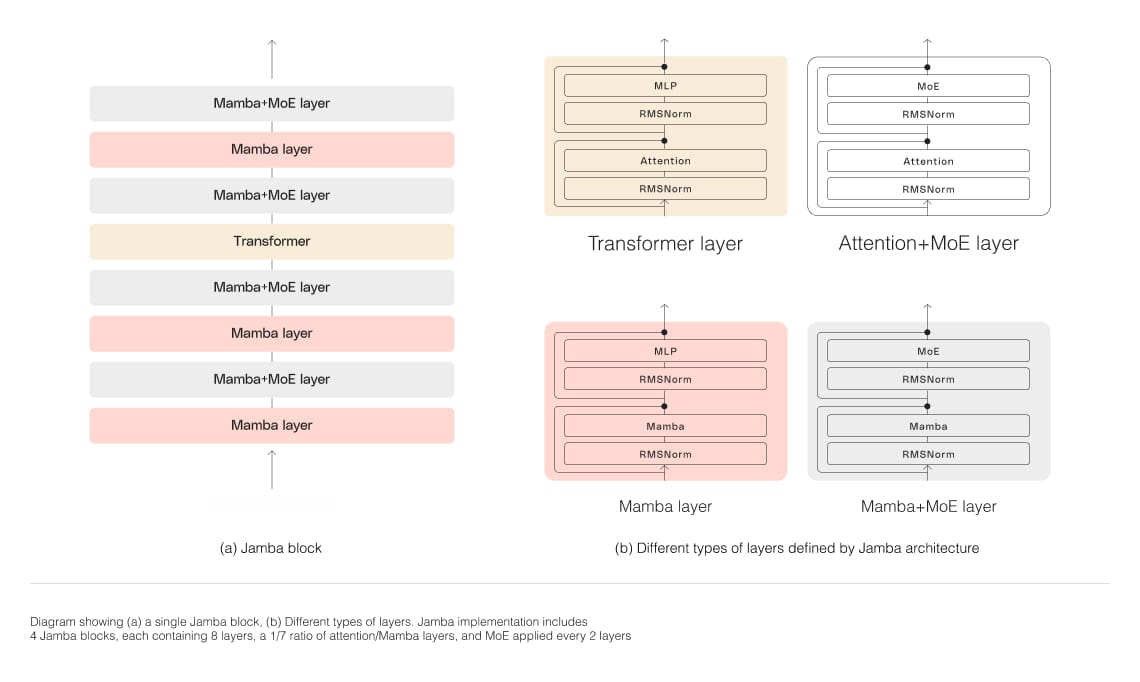
Jamba is AI21's first-of-its-kind hybrid SSM-Transformer model
Jamba's transformer architecture compensates for the limitations of its Mamba Structured State Space model (SSM) technology. Jamba supports a 256K-token context window, fits up to 140K context on a single GPU, and matches or outperforms other competitive models in its size class. Its hybrid architecture addresses the main drawbacks of traditional Transformer-only models: a large memory footprint and the loss of efficiency as context grows. Switching to a Mamba architecture is insufficient because it lacks attention over the whole context; without it, the technology struggles to yield high-quality outputs comparable to those of Transformer-only models. Thus, the Joint Attention and Mamba (Jamba) architecture combines Transformer, Mamba, and mixture-of-experts layers (MoE) to optimize memory, throughput, and performance. AI21 Labs released Jamba under an Apache 2.0 license with open weights to foster further development and experimentation. NVIDIA AI Enterprise software users can also deploy Jamba via the NVIDIA API catalog as an NVIDIA NIM inference microservice.
Skyflow secured an additional $30M from a Series B extension led by Khosla Ventures
The company is dedicated to providing data privacy solutions to ensure organizations and businesses handle sensitive data correctly. To do this, their main offering consists of API-accessible Data Privacy Vaults that add data privacy to an app in a similar way as Stripe can be used to add online payment support. Skyflow recently expanded the reach of its data privacy business by supporting AI-related technologies. Skyflow's LLM Privacy Vault enables its users to leverage LLMs without compromising data privacy by identifying and redacting data throughout the entire LLM lifecycle, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, limiting the number of users that can be exposed to sensitive data, and enabling compliance to regulation. Skyflow claims that LLM-related usage recently grew from 0 to 30%, indicating demand for data-management services specializing in data-hungry LLMs. Considering this, it is not unsurprising that Skyflow would be able to secure additional funding after its $45M Series B in 2021. The only thing that may strike as unconventional is that Skyflow withheld from calling this funding effort a Series C, labeling it as a Series B extension instead. Co-founder and CEO Anshu Sharma explains that the company learned that late-stage investors are holding back on the money they are willing to invest. Thus, aligning themselves with the profile of more active early-stage investors, Skyflow labeled its most recent round as a Series B extension.
Databricks introduced DRBX, its open general-purpose state-of-the-art LLM
In addition to setting a new state-of-the-art standard for open models, DBRX brings capabilities to the table that were previously restricted to closed-source models. Broadly, DBRX surpasses GPT-3.5's performance and is competitive with Gemini 1.0 Pro. Moreover, DBRX is performant at coding tasks, outclassing the specialized CodeLLaMA-70B. DRBX also features improved training and inference performance; contrasted with the previous-generation MPT models, DBRX achieves the same performance using nearly 4x less computing resources. DBRX's fine-grained mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture powers inference twice as fast as LLaMA2-70B, with a footprint 40% smaller than Grok-1 considering active and total parameter counts. Hosted on Mosaic AI Model Serving, DBRX generates up to 150 tokens per second/user. The base (DBRX Base) and fine-tuned (DBRX Instruct) model weights are available on Hugging Face under an open license. The model can also be deployed via API and Databricks customers can choose between training custom models from scratch or continuing from one of Databricks' checkpoints. Interested users can also take DBRX Instruct for a spin at Databricks' HF Space or browse the model repository on GitHub.
The Google.org Accelerator: Generative AI will fund non-profits developing AI-related technologies
The six-month accelerator program will provide the selected applicants with grants from its allocated $20 million fund, technical training, workshops, mentors, and guidance. Among the participating non-profits, Quill.org is a company creating AI-powered tools for student writing feedback and the World Bank is developing a generative AI app that facilitates development research. Tarjimly plans to use AI to accelerate its translation and interpretation services for non-profits, humanitarian workers, refugees, and immigrants. Benefits Data Trust wants to create assistants that support caseworkers in enrolling low-income applicants in public benefit programs, while mRelief is designing a tool to streamline the US SNAP benefits application process. Data indicates that most non-profits believe that AI aligns with their missions, but there are significant hurdles to overcome, especially regarding funding and training. Regardless, the signs of progress remain, as non-profit accelerator Fast Forward has reported that more than a third of participants in its latest round of selected applicants were AI companies, and independent efforts including AlgorithmWatch, JoyEducation, and Earth05 continue to emerge.
Profluent appointed key talent and secured $35M in funding
The AI-first protein design company has now secured a total of $44 million in funding, thanks to the $35 million financing led by Spark Capital, with backing from existing investors Insight Partners and Air Street Capital, and angel investors from industry-leading organizations such as OpenAI, Salesforce, Octant Bio and Google DeepMind. The initial $9 million was raised with support from Insight Partners, Air Street Capital, AIX Ventures, and Convergent Ventures. The company was founded to explore the possibility that AI could work as an interpreter helping us understand the language of life to go beyond traditional protein engineering, an approach it shares with other forays into protein prediction. The raised capital and the appointment of Hilary Eaton, Ph.D. as Chief Business Officer, and Peter Cameron, Ph.D. as VP and Head of Gene Editing will accelerate the Profluent platform's current focus on gene editing. Profluent expects AI to be capable of accurately tuning existing CRISPR scaffolds or even creating new personalized editing systems from scratch, meaning patients could be matched with a tool tailored to their particular needs. As part of the funding agreement, Former Head of Product at OpenAI Fraser Kelton and Spark Capital general partner Nabeel Hyatt will join the Profluent Board of Directors.
OpenAI shared some first impressions from creative experts on Sora and trusted partners on Voice Engine
Since the Sora early announcement, OpenAI committed to gathering feedback from creatives ranging from visual artists and designers to creative directors and filmmakers. A little over a month later, OpenAI has decided to share some feedback and several examples of the surveyed artists' work using Sora with the world. There is a consensus that, rather than have it try to replicate reality, Sora excels at bringing the impossible to life, as showcased by Air Head, shy kids' short film about a balloon man. Another point of agreement was that Sora frees the creative process from several technical, monetary, and even physical constraints, making it an excellent tool for fast prototyping, broadening the scope of the available creative outlets, and even providing new sources of inspiration to spark a well-known process.
Voice Engine is a model that receives text input and a 15-second audio sample to generate natural-sounding speech approximating the original sound of the sampled speaker. OpenAI has used Voice Engine to create the preset voices in the text-to-speech API, ChatGPT Voice, and Read Aloud. The company is aware of the potential for synthetic voice misuse and set out to start a dialogue regarding responsible use, along with a small-scale test in which trusted partners were given access to Voice Engine. Some early applications of the model include providing reading assistance to children and non-readers, translating content to expand access, aiding global community outreach, assisting non-verbal people, and helping patients recover their voices.
As part of the effort to start a conversation on responsible synthetic voice usage, those taking part in the Voice Engine test run agreed to OpenAI's usage policies, which explicitly forbid using the technology for non-consensual impersonation of individuals or organizations. It is also against policy to enable individual users to replicate their voices, and audiences need to be notified that they are interacting with AI-generated content. Regarding internal measures, Voice Engine's outputs are watermarked for origin tracing and are proactively monitored to see how they are used. Future broader measures endorsed by OpenAI are voice authentication measures "that verify that the original speaker is knowingly adding their voice to the service," and a "no-go list" for detecting and preventing the creation of voices sounding too similar to prominent figures. OpenAI has decided not to release Voice Engine yet, and as a complement to the safety measures outlined above, the company sees steps such as
- phasing out voice-based authentication,
- the continued development of policies that protect the use of individuals' voices in AI,
- reaching out to the public so they understand the possibility of encountering deceptive AI content, and
- accelerating watermarking and tracking technologies
as necessary to promote a safe, more adequate context for a broader release of technologies such as Voice Engine.
Eliyan Corporation, a pioneer in chiplet interconnect technology, secured a $60M Series B
The round was co-led by prominent investors Samsung Catalyst Fund and Tiger Global Management, with participation from Intel Capital, SK Hynix, Cleveland Avenue, Mesh Ventures, and others. The Series B round builds on the company's 2022 $40 million Series A round, further empowering Eliyan to tackle the most pressing challenges surrounding the design and manufacturing process of advanced, AI-focused chips using multi-die architectures in advanced packaging or standard organic substrates to achieve increasing levels of performance and power efficiency. In addition to die-to-die interconnection technology, the company's Universal Memory Interface enables a bandwidth-efficient connection to memory. This significantly increases the aggregate memory bandwidth per chip and reduces the die area required for memory interfaces.
San Jose, a California city, is experimenting with using AI to detect unhoused resident encampments
The city recently issued an open invitation to fit cameras on a municipal vehicle that periodically drives through sections of the city's District 10 since December. The cameras collect footage destined to train the companies' unwanted object detection algorithms. The pilot is currently developing the algorithm's capabilities to detect potholes and cars blocking bus lanes, with similar programs also being deployed in other US cities. However, San Jose's pilot on unhoused resident encampments is the first of its kind, and housing advocates worry that it could be used to punish or push out unhoused residents from the city. Companies involved in the San Jose pilot include Ash Sensors, Sensen.AI, Xloop Digital, Blue Dome Technologies, and CityRover. The vehicle's route currently includes places where unhoused residents often organize, including the city's only designated safe parking area for RVs, often used as homes. A representative for Ash Sensors stated the company had never experimented with encampment detection before and clarified it is training its algorithms to distinguish empty parked RVs from lived-in ones. Sensen.AI reported that its system detected 10 lived-in vehicles, and included OCR recognition of their license plate numbers. This is at odds with the claim that one of the metrics upon which the AI systems are assessed is their privacy-preserving features. To assuage the evergrowing concerns about potential persecution, San Jose IT department director Khaled Tawfik stated that the purpose of the pilot is not to recognize people, but unwanted objects.
Buddywise raised 3.5M EUR in its seed funding round to develop a real-time risk detection platform for the workplace
The round was co-led by J12 and Kvanted, with the participation of Eric Quidenus-Wahlforss, founder of Soundcloud. The Sweden-based startup has built a dataset of safety risks in the workplace using machine learning and computer vision. This data is leveraged to perform algorithmic analysis on footage collected from industrial customers' security cameras to detect potential risks that would otherwise go unnoticed. Once Buddywise's platform discovers a potential risk in a client's footage, it triggers an alert for the event to be promptly addressed. Buddywise is used across infrastructure and manufacturing sites in Sweden, Finland, Latvia, and Poland. The raised funds will be allocated to outreach, recruitment, and the company's further expansion across the continent. By further developing its platform, Buddywise hopes to have a positive impact that helps mitigate the thousands of non-fatal and hundreds of fatal workplace accidents that take place yearly in Europe.
Foundational announced its general availability
The data management platform integrates directly with Git, enabling developers to find, fix, and prevent data issues before deploying their code. Upon starting Foundational, its founders realized that data issues were not just about the difficulties preventing an understanding of the complete set of downstream dependencies at build-time, since dependency understanding cannot reliably confirm that a code change will introduce data issues. Moreover, confirmation that a code change will cause an issue requires going beyond dependencies to understanding the semantics, and being aware that data issues can have multiple sources. Finally, there is also the fact that data issues are not always about quality; they can also be about privacy impact, performance degradation, or even cost inflation. Then, there is the aggregated challenge of performing the pertinent analyses without leaving git. It is no small feat that Foundational has analyzed almost 60,000 pull requests in SQL, Python, and Scala, and will continue to perform what it does best at an even larger scale. Fortunately for the company, its general availability announcement was concurrent with its seed funding round announcement: the company raised $8 million in a seed funding round led by Viola Ventures and Gradient Ventures, with participation from Asymmetric Capital Partners and angel investors from industry leaders including Datadog, Intuit, Meta, and Wiz.
Gather AI secured $17M in a Series A round led by Bain Capital Ventures
The company helps customers solve supply chain issues by leveraging computer vision and AI to develop inventory monitoring solutions. Gather AI replaces the standard cycle counting via barcode scanning method for correcting inventory inaccuracies with drones that fly autonomously through warehouses and other storage facilities, scanning items 15x faster than traditional methods. The drones also collect richer data before automatically comparing it with the information displayed by the warehouse management system. According to the company, its customers see a 3-5x ROI, due to a 66% reduction in inventory inaccuracies. Gather AI will be able to scale its operations thanks to its recent Series A funding round where the company raised $17 million led by Bain Capital Ventures, backed by Tribeca Venture Partners, Dundee Venture Capital, Expa, and Bling Capital. The Series A brings Gather AI's total raised funding to $34 million.
Viam, the smart machine design and administration platform, announced its Series B funding round
Viam announced the successful closing of a $45 million Series B funding round which will fuel the company's next chapter. Viam's remarkable platform combines unexpected components, such as low-level hardware APIs, algorithms, cloud connectivity, fleet management, and AI, into one platform. This feature makes it the ideal driver for innovation across industries that do not necessarily intersect. The company has already been involved in noteworthy use cases, including insurance risk mitigation through data and automation, predictive maintenance for industrial machines, enabling open data sharing, and collecting marine life data to enhance vessels with marine life avoidance technologies. Viam's abstractness translates into features that can drive innovation in the most diverse industries, such as optionality, the ability to enhance existing assets with new features or create entirely new ones, and the appeal that attracts many developers to its platform.
Hume AI announced its successful Series B round and released its flagship Empathic Voice Interface (EVI)
Hume AI secured $50 million in a Series B round led by EQT Ventures to launch their Empathic Voice Interface (EVI), a conversational AI that understands emotional expressions through vocal tones to provide more natural voice interactions. EVI is powered by a novel multimodal generative AI that integrates LLMs and expression measures into a model that Hume calls an empathic large language model (eLLM). The empathic LLM lets EVI understand when its interlocutor is done speaking, and it can optimize its responses by adjusting its choice of words and the tone it delivers them with, based on context and the user's emotional expressions. Additionally to its detection and optimization capabilities, EVI also features a universal voice interface, interruptibility, and emotional text-to-speech. The company is also committed to safe and responsible AI development through The Hume Initiative, a non-profit developing guidelines for empathic AI with the collaboration of AI researchers, ethicists, social scientists, and legal scholars. In addition to EVI, Hume also launched its Expression Measurement API, a toolkit for measuring human emotional expression, and Custom Models, which predict user preference by using transfer learning on the data collected by the API. The company also grew its datasets to include data from over a million participants, doubled the size of its team, and published several papers in academic journals.
Researchers are examining a dual approach to treating sepsis that combines a blood test with AI
Sepsis is a condition where the body cannot respond properly to infection. Sepsis can quickly progress to septic shock, which can inflict fatal damage to several organs and is responsible for around 11 million deaths yearly. The research team analyzed the proteins associated with the immune response to sepsis to find patterns. The analysis yielded molecular signatures for septic shock, and organ damages used to train a model so it could predict which patients were more likely to go into septic shock and organ dysfunction. The patients were sorted into categories according to their risk level and the AI showed patients' risk level correlated with higher death rates. Experts believe that a dual approach like the one described could provide faster, more accurate diagnoses and additional tools to identify high-risk patients before they start developing potentially fatal complications. Although researchers are aware that, as with any similar research, the combined approach has to undergo further validation before widespread clinical use, they are also hopeful that a diagnostics tool like this one could be deployed worldwide as a new standard for early sepsis detection.
New York City launched a pilot program that deploys AI-enabled gun scanners in selected subway stations
Officials are looking for companies with expertise in weapon detection and will install the scanners after a mandatory 90-day waiting period. Once installed, the NYPD will evaluate the devices' effectiveness. The scanner demonstrated during the program launch came from Evolv, a publicly traded company surrounded by controversy after accusations that it had doctored its software testing results to make the devices appear more effective. Evolv is under investigation by the US trade and chief financial regulators. The company describes its weapon scanners as an "AI-driven system using safe, ultra-low frequency, electromagnetic fields, and advanced sensors to detect concealed weapons." The device demonstrated during the announcement beeped after a police officer with a holstered gun walked through it, but not after officers carrying cellphones and other electronic devices went through. The pilot program comes after two high-profile incidents in the subway system earlier this month. During the announcement, NYC Mayor Eric Adams stated that the city would independently analyze the scanners' accuracy.
Adobe unveils Firefly Services, a set of generative and creative APIs, tools, and services
Firefly Services grants enterprise developers access to Adobe's AI-powered features from tools like Photoshop so they optimize existing content creation workflows in their organization or create new ones from scratch. Adobe also launched Custom Models, a feature in its AI-first GenStudio that lets users customize Adobe's Firefly models. Firefly Services includes APIs for background removal, smart image cropping, automatic leveling, and several core Photoshop AI-powered features, such as Generative AI and Expand. Adobe has assured its customers that Firefly Services is a brand-safe product like its other AI-powered offerings. Thus, organizations can confidently deploy the Firefly Services tools to generate and customize branded content at scale.